The multi layer flex circuit refer to a flex circuit with more than 2 layer circuit layers. Three or more flexible conductive layers with flexible insulating layers between each one, which are interconnected by way of metallized hole through the vias/holes and plating to form a conductive path between the different layers, and external are polyimide insulating layers.
Normally a multilayer flexible circuit is a combination several double sided flex circuits and single layer flex circuit, so there’s not already existed flexible copper clad laminate. The multi-layers may or may not be continuously laminated together throughout the production process. If your design needs require maximum flexibility, continuous lamination may not be appropriate.
Multi-layer flexible circuit was made of polyimide is about at least 1/3 lighter than rigid FR4 PCB, but as there’re several layers, it loses the flexibility of single-sided, double-sided flexible PCB, but most of these products are not required for flexibility. Most popular multi-layers circuit are 4L and 6L and 8L. 10L or circuit more than 10L is seldom used in the market.
When to use & Feature of Multi-Layer Flex
Eliminating the need for complex welding processes, multi-layer flex circuits board have tremendous functional differences in terms of higher reliability, better thermal conductivity, and more convenient assembly performance. And also, it has excellent electrical properties such as a low dielectric constant. So multi-layer flexible circuits are an effective solution when following purpose & characteristics is needing:
- Unavoidable crossovers
- Elimination of crosstalk
- Ground and power plane applications
- Used for EMI, RF shielding applications
- Through-hole assembly
- Specific impedance controlled
- Up to 10 or more conductive layers
- Unbonded regions to increase flexibility in bend region
- Increased circuit density: Multilayer high circuit density system can handle multiple conductive layers to save space
- High components density
- Other customer-specified electrical requirements
- Ideal for the aerospace and defense markets
Multi Layer Flex Circuit Structure / Stack up
Here are stack up of a normal 4 layer flexible circuit:

ulti-layer flexible printed circuit board can be further divided into the following types:
1) Normal stack up: All the layers are laminated to each other, without separate between each layer, it loses its inherent flexibility after lamination. The more layers circuit has, the less flexibility circuit will be.
2) Unbonded/Separated stack up: Each layer, or several layers are separated from each other in the center portion, so they are unbonded in center area and electronically connected at the both end of flexible circuit. The flexibility is much better than normal stack up.
Multi-layer flexible printed circuit board can be further divided into the following types:
1) Normal stack up: All the layers are laminated to each other, without separate between each layer, it loses its inherent flexibility after lamination. The more layers circuit has, the less flexibility circuit will be.
2) Unbonded/Separated stack up: Each layer, or several layers are separated from each other in the center portion, so they are unbonded in center area and electronically connected at the both end of flexible circuit. The flexibility is much better than normal stack up.
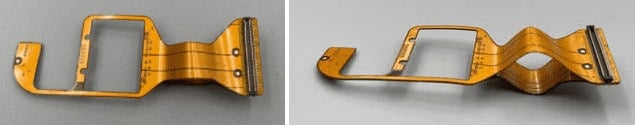
Multi Layer Flex Circuit Materials:
Multi layer flex also allows for localized areas where stiffeners, pins, connectors, and components may be added, so material is the same like double sided flex circuits, all has core material, coverlay, stiffeners, PSA EMI/RF shielding.
Key Capabilities:
- Multilayer circuitry-from 3 to 14+ layers
- Min LW/LS: 4mil/4mil
- Adhesive-based and adhesiveless constructions, including thermoplastic and thermoset stiffener attachment.
- Polyimide substrates: 1/2mil – 4mil
- Copper: 1/3OZ – 2OZ, RA or ED type
- Stiffeners include Polyimide (0.075-0.20mm), FR4 (0.15-2.0mm), and punched or formed metal parts (0.075-1.0mm)
- Low-cost, conventional fabrication and lamination completed with PTH based plating
- Screened inks, photo-imageable soldermasks, or laminated coverlay dielectrics
- Surface finishes: ENIG, electroplated nickel/gold, immersion silver, tin,
- EMI Shielding



