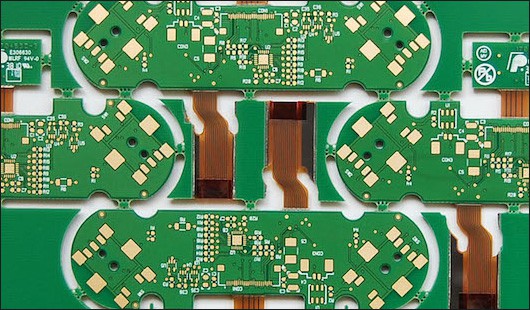
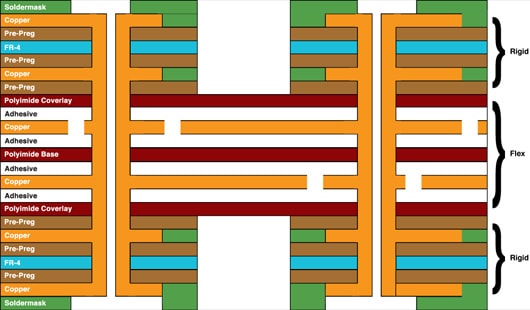
Rigid-flex PCB is a composite board of rigid PCB and flexible PCB, which is suitable for various applications. A typical rigid-flex PCB circuit includes two or more conductive layers, each of which contains a flexible or rigid insulating material-the outer layer may have exposed pads or cover layers. Conductors can be found on the rigid layer, and plated through holes can be found on both the rigid and flexible layers.
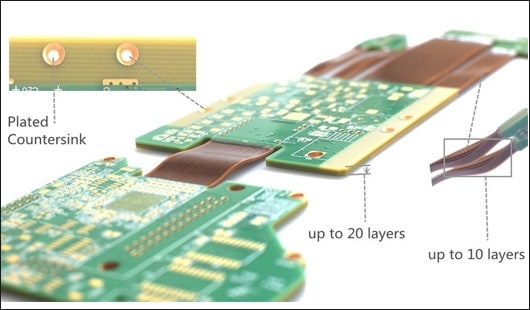
Advantages
1) It is easier to assemble smaller size and more components together than rigid PCB, reducing the overall system cost;
2) Require fewer interconnections and related parts and components, shorten assembly time and reduce parts management and inventory costs;
3) Shorten the distance and increase the signal transmission speed. Reduce the transmission of the medium, Improve signal accuracy, and improve the reliability of manufacturing.
Like all types of flexible circuit boards, rigid-flexible PCBs work well even in the harshest environments, especially in high-temperature conditions. Rigid flexible boards are also easy to test and very suitable for prototyping.
Applications:
Rigid-flexible PCBs have been widely used in smart devices, communication industries, and medical equipment. In consumer products, rigid-flexible PCB does not only maximizes space and weight but also greatly improves reliability, thereby eliminating many needs for solder joints and fragile wiring that are prone to connection problems. Rigid-flex PCBs can be used for almost all advanced electrical applications, including test equipment, tools, and automobiles.